Insert Molding Vs Overmolding: Key Differences & Applications
Introduction: Molding Vs Overmolding: The Major Differences
Facing a serious decision between insert molding vs overmolding, manufacturers have to make a tough decision when dealing with high-precision plastic and multi-material parts. Both procedures improve product functionality, durability, and beauty; however, each possesses its own benefits relative to use. Your electronic housings, automotive, or medical devices, regardless, you need to be able to determine the technical and commercial distinctions that can lead to the selection of the appropriate solution.
We are the SunOn Mould and focus on producing custom molded parts with the application of a range of innovative multi-material techniques of molding techniques, such as insert molding, TPU overmolding, and two-shot molding.
What is Insert Molding?
Insert molding is an accurate process, where metal or plastic inserts are put into a mold, and molten plastic is injected around them. This forms one whole element, and the insert is incorporated until it becomes a permanent piece of the end product.
Insert Molding is used in the following applications:
- Electronics components: circuit board, connector, and housing.
- Auto components: thread metal inlaid dashboards, switches, and handles.
- Industrial equipment: tool slips and guards.
Benefits of Insert Molding:
Improved Material Bonding: There is a firm bond between the inserts and the molded plastic.
Less Assembly Processes: Does not require secondary assembly or fasteners.
High Precision: Suitable when precise components with tight tolerances and thermoplastic resin molding are needed.
Material Versatility: Accepts metals, reinforced plastics, and thermoplastic elastomers.
What is Overmolding?
Multi-material injection molding is used in overmolding, where one material is injection molded over a core, which is a primary material. This is common in the production of soft-touch grips, ergonomic handles, and protective housings.
Overmolding has been applied in:
- Electronics: phone cases, keypads, and wearable technology.
- Car: soft-touch tool grips and dashboard handles.
- Medical equipment: ergonomic casings and cases.
Advantages of Overmolding:
Better Ergonomics and Grip: Soft materials such as TPU or silicone offer a better touch feel.
Durable Multi-Material Bonding: Cures a one-piece, which has both practical and aesthetic characteristics.
Low-Cost Manufacture: Saves labor and assembly: Combines several parts at once.
Design Flexibility: Accommodates multi-shot molding and TPU overmolding, as well as complicated geometries.
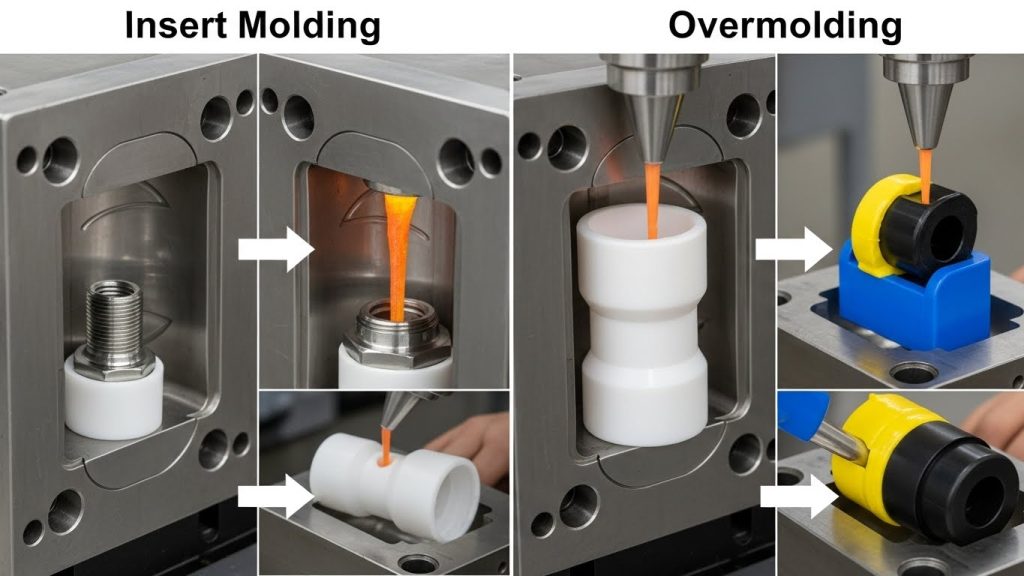
The Major Differences Between Insert Molding and Overmolding
Material Bonding:
- Insert molding is a mechanically bonded connection of metal or plastic inserts.
- The secondary surface layer formed is overmolding onto the primary substrate, commonly with thermoplastic elastomers or TPU.
- Applications Focus:
- Insert molding is preferred in cases of structural integrity and threaded parts.
- Ergonomics, aesthetics, and protective coating are best done by overmolding.
Tooling and Mold Design:
- Precision design of the mold cavity is essential when using inserts in insert molding; the design of the mold cavity must be such a way that the inserts can fit in the correct position.
- Multi-shot or two-shot molds are used in overmolding to minimize transitions between materials and surface finishing.
Production Efficiency:
- Both processes decrease steps in the assembly; however, overmolding can be used with a faster cycle time with robotic placement of the insert or automated processes.
Cost Considerations:
- Including o Insert molding could be more expensive to set up in the beginning because of the insert handling requirements.
- The production of high volumes of soft-touch grip or TPU products may be economical and only requires overmolding.
Electronics Components, Overmolding vs. Molding Insertion
Both processes are used by electronics manufacturers, but to achieve various purposes:
Insert Molding: Molds Circuit boards with plastic housings that have metal contacts or threaded inserts.
Overmolding: Provides impact protection in the form of protective TPU or silicone over-molding.
The benefits of integrating the two:
- Manufactures long-lasting soft-touch electronics enclosures.
- Lessens the risk of part loosening or failure.
- Maximizes aesthetics by multi-material design.
- Molding vs Rubber Injection Molding in the automobile industry.
The Car Market Requires High Durability and Ergonomics:
Insert Molding: This method is applied in the case of metal inserts in dashboards, gear handles, and control switches to ensure they are stronger and more precise.
Overmolding: Produces soft-touch grips, seals, and covers to keep the user comfortable and attractive.
Manufacturers can use complex and multi-material automotive parts by combining insert and overmolding processes and taking advantage of the 2K Injection Mould technology of SunOn.
Material Differences Between Insert Molding and Overmolding
TPU vs Insert Molding: TPU overmolding is soft touch, impact-resistant, and flexible. Rigid or structural parts should be subjected to insert molding.
Plastic-to-Metal Bonding: Metal Inserts Plastic insert molding is the best for use with metal inserts, but overmolding metal inserts may also be used to provide additional protection.
Thermoplastic Elastomers: Specialty thermoplastics, heat-stable plastics, and reinforced polymers can be used in both processes to make high-performance parts.
Technical Factors to Be Considered
Mold Cavity Design: The correct design is necessary to achieve precision, eliminate flash, and maintain the insert position or adhesion of the overmold.
Pressure Optimization on Injection: It is essential to have a consistent flow of the material and good bonding strength.
Shrinkage Compensation: This is required to ensure that plastic shrinkage and placement tolerances of the insert are taken into consideration.
Cycle Time Efficiency: Multi-shot molding, robotic handling, and automated systems are used to optimize it.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics: Overmolding can provide smooth ergonomic surfaces, whereas insert molding is concerned with structural accuracy.
Comparison of Insert Molding Vs. Overmolding
In deciding to use either of the two methods, consider:
- Part Functionality: Structural vs ergonomic.
- Production Volume: Low-volume prototypes -high volume mass production.
- Material Requirement: TPU, silicone, thermoplastic elastomers, metals.
- Reduction Assembly Needs: Reduce the number of fasteners and secondary assembly.
- Cost and Tooling: First tooling vs lifecycle cost efficiency.
In SunOn, OEMs and manufacturers are guided through the maze of finding the most appropriate insert molding/overmolding mix, in terms of electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products.
Commercial Advantages of Insert Molding and Overmolding
- Saves time and labor, and assembly.
- The part increases durability and life span.
- Allows aesthetics and ergonomics multi-material design.
- Facilitates mass production of quality output.
- Sustains ISO-certified manufacturing standards.
Part of the custom molded inserts, overmolded components, or multi-material integrated solutions, SunOn provides high-precision and economical results.
Conclusion
The critical factor in the field of manufacturing that should not be overlooked is the knowledge of what is meant by insert molding vs overmolding in order to produce a high-quality, durable, and aesthetically appealing product. Both techniques have special benefits of material bonding, ergonomics, and assembly efficiency.
Using the competence of SunOn in terms of plastic injection molding, multi-material molding, TPU overmolding, and 2K injection molds, companies can gain precision, durability, and aesthetic perfection in electronics, automobiles, medical, and consumer products.
Learn more about our complete line of services with the SunOn Mould and find out how your product development and production efficiency could be changed with the help of the custom insert molding and overmolding solutions.

